Progressive Web Apps on iOS are here ?
With iOS 11.3, Apple has silently added support for the basic set of new technologies behind the idea of “Progressive Web Apps” (PWAs). It’s time to see how they work, what are their abilities and challenges, and what do you need to know if you already have a published PWA.
⚠️ Updated version of this article ⏩ firt.dev

Update: this article is still 100% valid for iOS 12.
If you came here and you still don’t know what a PWA is, let’s start saying there is no unique or precise definition. But it’s an app created with Web technologies that −without packaging or signing− can work offline and can optionally be installed in the operating system where it will look and act like any other app.
(Ad: I’m teaching Mastering PWA training at different events and cities)
There is no App Store process involved in most platforms−only Edge/Windows 10 is currently forcing PWAs to be in the store.
So you are right, you can now install apps on iOS without App Store approval. That’s probably one reason Apple didn’t mention at all about this new ability; they might not want to confuse users. Not even the release notes on Safari mention the technologies.

Update: iOS 12.2 is now released with some changes; check also this article for complement content: https://medium.com/@firt/whats-new-on-ios-12-2-for-progressive-web-apps-75c348f8e945
Wasn’t Apple the creator of PWAs anyway?
Let’s be honest here; while Google with the Chrome team coined the term PWA, the idea was initially available on Safari at the original iPhone OS. In 2007, Steve Jobs announced “one more thing” in the WWDC: how to develop apps for the original iPhone and it was, surprise, web apps! The App Store was not on the original roadmap, and the native SDK wasn’t available during the first year of the device. From an Apple’s perspective PWAs even today are just “web apps from the home screen,” and the icon is something referred as a WebClip.
If you want, check the Fluent Conference keynote I delivered last year; I mentioned this for one minute at 10:50https://cdn.embedly.com/widgets/media.html?src=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fembed%2FEFGltzFSK-c%3Fstart%3D651%26feature%3Doembed%26start%3D651&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3DEFGltzFSK-c&image=https%3A%2F%2Fi.ytimg.com%2Fvi%2FEFGltzFSK-c%2Fhqdefault.jpg&key=a19fcc184b9711e1b4764040d3dc5c07&type=text%2Fhtml&schema=youtubeJump to 10:50 to see the mention to Apple and PWAs in 2007
It’s also true that the idea didn’t get too much attention 11 years ago and Apple forgot to update that platform, so while still there for 10+ years it was buggy and inconsistent. A few years later other platforms cloned the idea including the MeeGo Browser on Nokia N9 and then Chrome on Android.
Chrome helped to evolve the technologies to offer a better experience, mostly with Service Workers and Web App Manifest specs. Starting from iOS 11.3 today (March, 30th 2018) Apple is matching Chrome, Firefox, Samsung Internet, UC Browser and Opera (mostly on Android only) supporting these two specs. Other browsers on desktop support Service Workers but Web App Manifest support is in the works for this year.

Wait there, so the app didn’t pass any App Store quality test, right? ?
Yes, that’s correct. However, the app will run only under the browser’s or the Web Platform security and execution model. That means you can “publish” apps that are not approved in the store, such as an internal app for your company’s employees (and yes, also adult content), but you can’t access pure native features, such as Face ID on iPhone X or ARKit for augmented reality. Or at least, you need to wait for the Web Platform to catch those new features.
The PWA can run inside Safari as any website or in standalone mode, like any other app in the system. If you are wondering if PWAs are using the Web View, that’s not the case from Safari or the installed icon, but it will be the case while browsing in other browsers or within Facebook with its In-App browser.
Abilities of PWAs on iOS
With the Web Platform on iOS you can access:
- Geolocation
- Sensors (Magnetometer, Accelerometer, Gyroscope)
- Camera
- Audio output
- Speech Synthesis (with headsets connected only)
- Apple Pay
- WebAssembly, WebRTC, WebGL as well as many other experimental features under a flag.

Limitations compared with native iOS apps
- The app can store offline data and files only up to 50 Mb
- If the user doesn’t use the app for a few weeks, iOS will free up the app’s files. The icon will still be there on the home screen, and when accessed the app will be downloaded again
- No access to some features, such as Bluetooth, serial, Beacons, Touch ID, Face ID, ARKit, altimeter sensor, battery information
- No access to execute code while in the background
- No access to private information (contacts, background location) and also no access to native social apps
- No access to In App Payments and many other Apple-based services
- On iPad, no access to work with Side or Split Views sharing the screen with other apps, PWAs will always take the whole screen
- No Push Notifications, no icon badge or Siri integration

What PWAs can do on Android and not on iOS
- On Android you can store more than 50 Mb
- Android doesn’t delete the files if you don’t use the app, but it can delete the files under storage pressure. Also, if installed or used a lot by the user the PWA can request Persistent Storage
- Bluetooth access for BLE devices
- Web Share for accessing native share dialog
- Speech Recognition
- Background Sync and Web Push Notifications
- Web App Banner to invite the user to install the app
- You can customize (a little bit) the splash screen and the orientations you want
- With WebAPK and Chrome, users can’t install more than one instance of a PWA
- With WebAPK and Chrome, the PWAs appears under Settings and you can see data usage; on iOS everything appears under Safari
- With WebAPK and Chrome, the PWA manages intents for its URL, so if you get a link to the PWA, it will be opened in standalone mode and not within the browser’s window.
What PWAs can do on iOS and not on Android
- Users can change icon’s name before installing it
- They can be configured in a configuration profile, so corporate users can receive PWAs shortcuts from the company (that’s a good one!). Safari uses the term WebClip for this feature; however it doesn’t seem to be reading the Web App Manifest (according to the documentation)

But if there is no App Store, how do you install a PWA? ⚠️
That’s one of the most significant challenges on iOS as there will be no prompts or invitations from Safari (known as Web App Banners on Android). So the user has to go to your PWA URL somehow within Safari and then manually press the Share icon and then “Add to Home Screen.” There will be no indication that a website you are visiting is a PWA.

Also, additional pseudo-browsers available in the App Store, such as Chrome, Firefox, Brave or Edge won’t be able to install a PWA or use Service Workers.
Once it’s installed, it will look like any other icon on the home screen. There will be no 3D Touch menu for it though. And if you install the same PWA again, you will have another icon pointing to the same PWA (fortunately, the installed files will be shared).
Also, a lot of web apps have a link to install the native app from the App Store, and that is still showing even inside the PWA, such as the Tinder example:

I already have a PWA, will it work on iOS right away?
Your PWA will be available for installation right away after your users update to iOS 11.3. You don’t need to opt-in for iOS. Every PWA is available for installation. But that doesn’t mean that everything will work as expected.

If you are reading this you may have already seen my previous article while in beta: Cupertino we have a problem. Unfortunately, most of the bugs and challenges I’ve been during betas are still here with us in the final version ?

What won’t work
- The display: fullscreen and display: minimal-ui won’t work on iOS; fullscreen will trigger standalone, and minimal-ui will be just a shortcut to Safari. You can get something similar to fullscreen (the status bar will exist but over your app) using the cover-fit viewport extension or a deprecated meta tag though.
- If you rely on Background Sync you should have a backup implementation
- No way to lock the orientation of your PWA
- The theme-color to style the status bar won’t work; you can use the deprecated meta tag for black or white status bars, or you can use a CSS/HTML trick to emulate a theme-color.

- If your PWA doesn’t have back gestures or buttons within the app’s UI the user won’t be able to navigate between screens
- Your Android icon might look terrible on iOS as Apple doesn’t support transparent icons, so check it out.
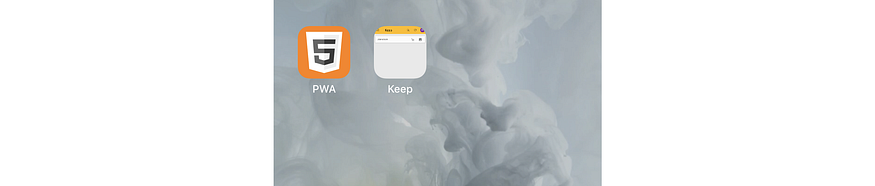
- Also, iOS is not taking the icons from the Web App Manifest, but from the apple-touch-icon link. If you don’t provide the link tag, a screenshot will be used for the icon (see Google Keep PWA example)
- There is no splash screen, so most color properties from the manifest are ignored
- No manifest events will be fired, so if you are tracking installation through these channels, it won’t work on iOS (but you can check navigator.standalone instead).
What to have in mind
- Your PWA won’t keep state between sessions, if the user gets out of a PWA, it will be restarted when coming back, so if you need the user to validate an email, SMS or do a two-factor authentication, have that in mind to offer a proper solution.

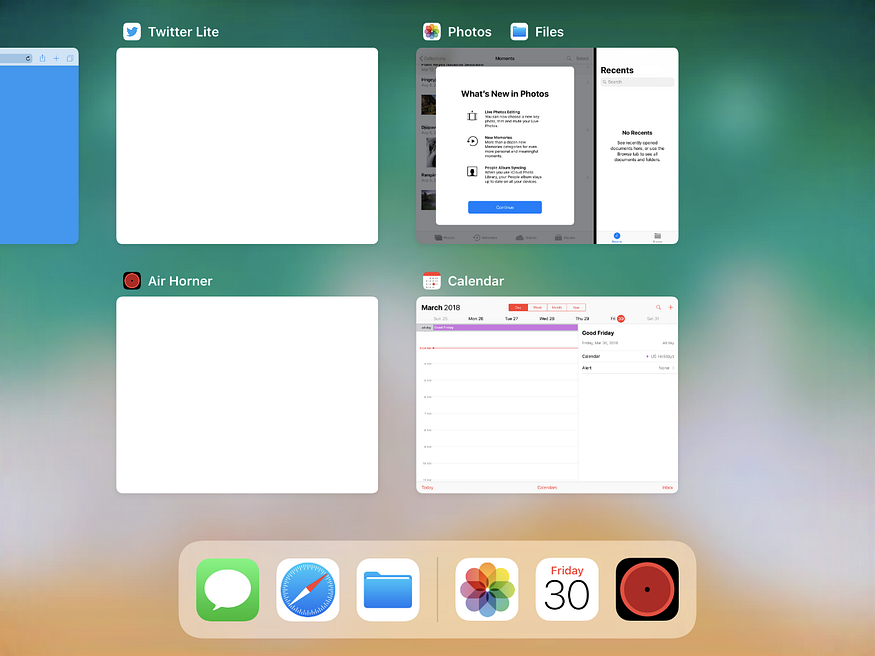
- PWAs in the history don’t have any screenshot so they all look like white screens unfortunately ?
- There are bugs when your app runs in standalone mode. Don’t rely on Safari for testing.
https://medium.com/@firt/progressive-web-apps-on-ios-are-here-d00430dee3a7
